The Netherlands
Related Categories:
 Symbols of Holland
Symbols of HollandThe Dutch are not overtly patriotic, except on special events. As a result, the Dutch flag is not a very common sight in Holland, and is usually only flown from political buildings or tourist attractions.
www.filibustercartoons.com/
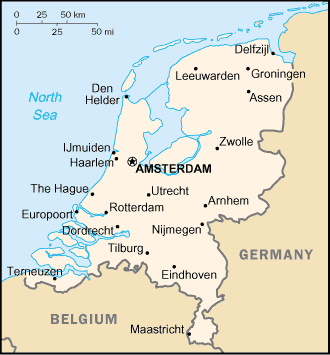
Provinces and municipalities of the Netherlands.
www.fotw.us/
The Netherlands is often referred to by the name Holland. This terminology is not correct, as the provinces of North and South Holland in the western Netherlands are only two of the country's twelve provinces.
en.wikipedia.org/
The Dutch are primarily of Germanic stock with some Gallo-Celtic mixture. Their small homeland frequently has been threatened with destruction by the North Sea and has often been invaded by the great European powers.
Julius Caesar found the region which is now the Netherlands inhabited by Germanic tribes in the first century B.C. The western portion was inhabited by the Batavians and became part of a Roman province; the eastern portion was inhabited by the Frisians. Between the fourth and eighth centuries A.D., most of both portions were conquered by the Franks. The area later passed into the hands of the House of Burgundy and the Austrian Habsburgs. Falling under harsh Spanish rule in the 16th century, the Dutch revolted in 1558 under the leadership of Willem of Orange. By virtue of the Union of Utrecht in 1579, the seven northern Dutch provinces became the Republic of the United Netherlands.
During the 17th century, considered its "golden era," the Netherlands became a great sea and colonial power. Among other achievements, this period saw the emergence of some of painting's "Old Masters," including Rembrandt and Hals, whose works--along with those of later artists such as Mondriaan and Van Gogh--are today on display in museums throughout the Netherlands and the world.
The country's importance declined, however, with the gradual loss of Dutch technological superiority and after wars with Spain, France, and England in the 17th and 18th century. The Dutch United Provinces supported the Americans in the Revolutionary War. In 1795, French troops ousted Willem V of Orange, the Stadhouder under the Dutch Republic and head of the House of Orange.
Following Napoleon's defeat in 1815, the Netherlands and Belgium became the "Kingdom of the United Netherlands" under King Willem I, son of Willem V of Orange. The Belgians withdrew from the union in 1830 to form their own kingdom. King Willem II was largely responsible for the liberalizing revision of the constitution in 1848.
The Netherlands prospered during the long reign of Willem III (1849-90). At the time of his death, his daughter Wilhelmina was 10 years old. Her mother, Queen Emma, reigned as regent until 1898, when Wilhelmina reached the age of 18 and became the monarch.
The Netherlands proclaimed neutrality at the start of both world wars. Although it escaped occupation in World War I, German troops overran the country in May 1940. Queen Wilhelmina fled to London and established a government-in-exile. Shortly after the Netherlands was liberated in May 1945, the Queen returned. Crown Princess Juliana acceded to the throne in 1948 upon her mother's abdication. In April 1980, Queen Juliana abdicated in favor of her daughter, now Queen Beatrix. Crown Prince Willem Alexander was born in 1967.
Elements of the Netherlands' once far-flung empire were granted either full independence or nearly complete autonomy after World War II. Indonesia formally gained its independence in 1949, and Suriname became independent in 1975. The five islands of the Netherlands Antilles (Curacao, Bonaire, Saba, St. Eustatius, and a part of St. Maarten) and Aruba are integral parts of the Netherlands realm but enjoy a large degree of autonomy.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon

