Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
Related Categories:
 Sri Lanka National Flag
Sri Lanka National FlagThe Symbol of Inequality and Separation.
www.sangam.org/
The National Flag of Sri Lanka represents the country and her heritage as rallying device that integrates the minorities with the majority race.
www.gov.lk/
These ancient flags represent the many different kingdoms, provinces and districts that existed in our country at some time, as well as the different chiefs who ruled the country and those assigned to the various temples.
www.sundayobserver.lk/
Description of the Flag, Construction sheet, The Flag in the National Constitution, History.
www.fotw.us/
Due to its location in the path of major sea routes, Sri Lanka is a strategic naval link between West Asia and South East Asia, and has been a center of Buddhist religion and culture from ancient times. Today, the country is a multi-religious and multi-ethnic nation, with nearly a third of the population following faiths other than Buddhism, notably Hinduism, Christianity and Islam.
en.wikipedia.org/
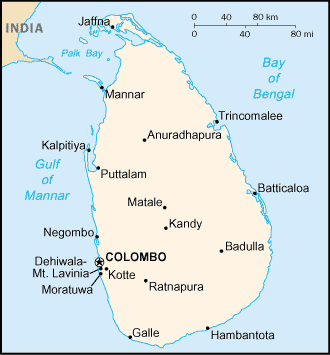
The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka (formerly known as Ceylon) is an island in the Indian Ocean about 28 kilometers (18 mi.) off the southeastern coast of India with a population of about 19 million. Density is highest in the southwest where Colombo, the country's main port and industrial center, is located. The net population growth is about 1.3%. Sri Lanka is ethnically, linguistically, and religiously diverse.
Sinhalese make up 74% of the population and are concentrated in the densely populated southwest. Ceylon Tamils, citizens whose South Indian ancestors have lived on the island for centuries, total about 12% and live predominantly in the north and east.
Indian Tamils, a distinct ethnic group, represent about 5% of the population. The British brought them to Sri Lanka in the 19th century as tea and rubber plantation workers, and they remain concentrated in the "tea country" of south-central Sri Lanka. In accordance with a 1964 agreement with India, Sri Lanka granted citizenship to 230,000 "stateless" Indian Tamils in 1988. Under the pact, India granted citizenship to the remainder, some 200,000 of whom now live in India. Another 75,000 Indian Tamils, who themselves or whose parents once applied for Indian citizenship, now wish to remain in Sri Lanka. The government has stated these Tamils will not be forced to return to India, although they are not technically citizens of Sri Lanka. In October of 2003, an act of Parliament granted citizenship to several thousand of these "tea estate" Tamils.
Other minorities include Muslims (both Moors and Malays), at about 7% of the population; Burghers, who are descendants of European colonists, principally from the Netherlands and the United Kingdom (U.K.); and aboriginal Veddahs. Most Sinhalese are Buddhist; most Tamils are Hindu. The majority of Sri Lanka's Muslims practice Sunni Islam. Sizable minorities of both Sinhalese and Tamils are Christians, most of whom are Roman Catholic. The 1978 constitution, while assuring freedom of religion, grants primacy to Buddhism.
Sinhala, an Indo-European language, is the native tongue of the Sinhalese. Tamils and most Muslims speak Tamil, part of the South Indian Dravidian linguistic group. Use of English has declined since independence, but it continues to be spoken by many in the middle and upper middle classes, particularly in Colombo. The government is seeking to reverse the decline in the use of English, mainly for economic but also for political reasons. Both Sinhala and Tamil are official languages.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon

