Republic of Armenia
Related Categories:
 Flag of Armenia
Flag of ArmeniaThree equal horizontal bands of red (top), blue, and orange. |
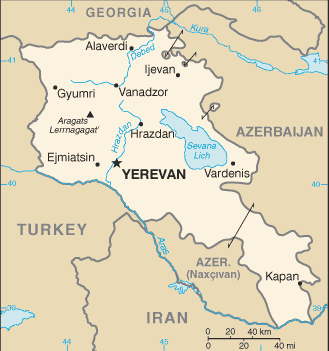 General information about the Republic of Armenia
General information about the Republic of ArmeniaFlag, Coat of Arms, Anthem, Constitution.
www.gov.am/
National symbols, coat of arms.
www.fotw.us/
The Coat of Arms of Armenia consists of an eagle and a lion supporting a shield.
en.wikipedia.org/
Ethnic groups in Armenia include Armenians (95%), Kurds, Russians, Greeks, and others. More than 90% of the population is nominally affiliated with the Armenian Apostolic Church. Languages are Armenian (96%), Russian, and others.
Armenia first emerged into history around 800 BC as part of the Kingdom of Urartu or Van, which flourished in the Caucasus and eastern Asia Minor until 600 BC. After the destruction of the Seleucid Empire, the first Armenian state was founded in 190 BC. At its zenith, from 95 to 65 BC, Armenia extended its rule over the entire Caucasus and the area that is now eastern Turkey, Syria, and Lebanon. For a time, Armenia was the strongest state in the Roman East. It became part of the Roman Empire in 64 BC and adopted a Western political, philosophical, and religious orientation.
In 301 AD, Armenia became the first nation to adopt Christianity as a state religion, establishing a church that still exists independently of both the Roman Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches. During its later political eclipses, Armenia depended on the church to preserve and protect its unique identity. From around 1100 to 1350, the focus of Armenian nationalism moved south, as the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, which had close ties to European Crusader states, flourished in southeastern Asia Minor until conquered by Muslim states.
Between the 4th and 19th centuries, Armenia was conquered and ruled by, among others, Persians, Byzantines, Arabs, Mongols, and Turks. For a brief period from 1918 to 1920, it was an independent republic. In late 1920, the communists came to power following an invasion of Armenia by the Red Army, and in 1922, Armenia became part of the Trans-Caucasian Soviet Socialist Republic. In 1936, it became the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic. Armenia declared its independence from the Soviet Union on September 21, 1991.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
