State of Brunei, Abode of Peace
Related Categories:
 Brunei - Fotw
Brunei - FotwFlags and Coat of Arms.
www.fotw.us/flags/bn.html Brunei - wikipedia.org
Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah of Brunei, whose title has passed within the same dynasty since the fifteenth century, is the head of state and head of government in Brunei. The Sultan is advised by several councils and a cabinet of ministers although he is effectively the supreme ruler.
en.wikipedia.org/
Many cultural and linguistic differences make Brunei Malays distinct from the larger Malay populations in nearby Malaysia and Indonesia, even though they are ethnically related and share the Muslim religion.
Brunei has hereditary nobility, carrying the title Pengiran. The Sultan can award to commoners the title Pehin, the equivalent of a life peerage awarded in the United Kingdom. The Sultan also can award his subjects the Dato, the equivalent of a knighthood in the United Kingdom, and Datin, the equivalent of damehood.
Bruneians adhere to the practice of using complete full names with all titles, including the title Haji (for men) or Hajah (for women) for those who have made the Haj pilgrimage to Mecca. Many Brunei Malay women wear the tudong, a traditional head covering. Men wear the songkok, a traditional Malay cap. Men who have completed the Haj can wear a white songkok.
The requirements to attain Brunei citizenship include passing tests in Malay culture, customs, and language. Stateless permanent residents of Brunei are given International Certificates of Identity, which allow them to travel overseas. The majority of Brunei's Chinese are permanent residents, and many are stateless. An amendment to the National Registration and Immigration Act of 2002 allowed female Bruneian citizens for the first time to transfer their nationality to their children.
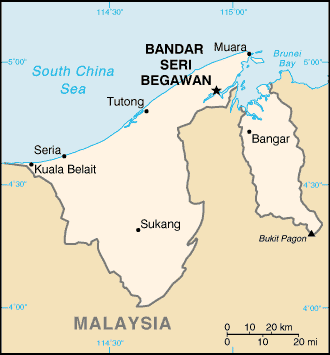
Oil wealth allows the Brunei Government to provide the population with one of Asia's finest health care systems. Malaria has been eradicated, and cholera is virtually nonexistent. There are five general hospitals--in Bandar Seri Begawan, Tutong, Kuala Belait, Bangar, and Seria--and there are numerous health clinics throughout the country.
Education starts with preschool, followed by 6 years of primary education and up to 7 years of secondary education. Nine years of education are mandatory. Most of Brunei's college students attend universities and other institutions abroad, but approximately 3,674 (2005) study at the University of Brunei Darussalam. Opened in 1985, the university has a faculty of more than 300 instructors and is located on a sprawling campus overlooking the South China Sea.
The official language is Malay, but English is widely understood and used in business. Other languages spoken are several Chinese dialects, Iban, and a number of native dialects. Islam is the official religion, but religious freedom is guaranteed under the constitution.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon

