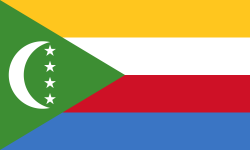
Union of the Comoros
Related Categories:
 Comoros - Fotw
Comoros - FotwThe colors of the horizontal stripes stand for the four islands.
www.fotw.us/
The Comoros is notable for its diverse culture and history, as a nation formed at the crossroads of many civilizations.
en.wikipedia.org/
People
The Comorans inhabiting Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Moheli (86% of the population) share African-Arab origins. Islam is the dominant religion, and Koranic schools for children reinforce its influence. Although Arab culture is firmly established throughout the archipelago, a substantial minority of the citizens of Mayotte (the Mahorais) are Catholic and have been strongly influenced by French culture.
The most common language is Shikomoro, a Swahili dialect. French and Arabic also are spoken. About 57% of the population is literate.
History
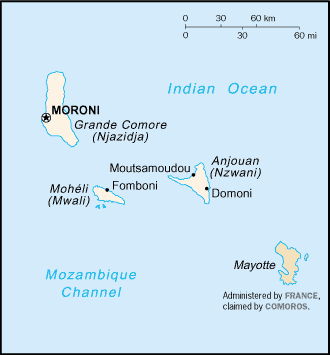
Over the centuries, the islands were invaded by a succession of diverse groups from the coast of Africa, the Persian Gulf, Indonesia, and Madagascar. Portuguese explorers visited the archipelago in 1505. "Shirazi" Arab migrants introduced Islam at about the same time. Between 1841 and 1912, France established colonial rule over Grande Comore, Anjouan, Mayotte, and Moheli and placed the islands under the administration of the governor general of Madagascar. Later, French settlers, French-owned companies, and wealthy Arab merchants established a plantation-based economy that now uses about one-third of the land for export crops. After World War II, the islands became a French overseas territory and were represented in France's National Assembly. Internal political autonomy was granted in 1961. Agreement was reached with France in 1973 for Comoros to become independent in 1978. On July 6, 1975, however, the Comoranparliament passed a resolution declaring unilateral independence. The deputies of Mayotte abstained. As a result, the Comoran Government has effective control over only Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Moheli. Mayotte remains under French administration.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon