The Dominican Republic
Related Categories:
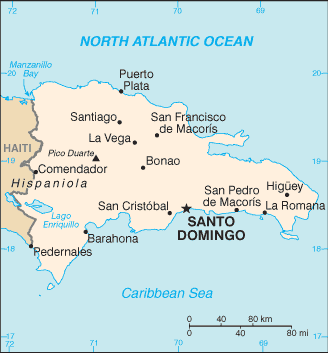
 The Dominican Republic Coat of Arms
The Dominican Republic Coat of Arms |
Flags, Coat of Arms.
www.fotw.us/flags/do.html Dominican Republic - wikipedia.org
Dominicans sometimes refer to their country as Quisqueya, a name for Hispaniola that is debated to have been used by indigenous Taíno people meaning "mother of all lands".
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
People
About half of Dominicans live in rural areas; many are small landholders. Haitians form the largest foreign minority group. All religions are tolerated; the state religion is Roman Catholicism.
History
The island of Hispaniola, of which the Dominican Republic forms the eastern two-thirds and Haiti the remainder, was originally occupied by Tainos, an Arawak-speaking people. The Tainos welcomed Columbus in his first voyage in 1492, but subsequent colonizers were brutal, reducing the Taino population from about 1 million to about 500 in 50 years. To ensure adequate labor for plantations, the Spanish brought African slaves to the island beginning in 1503.
In the next century, French settlers occupied the western end of the island, which Spain ceded to France in 1697, and which, in 1804, became the Republic of Haiti. The Haitians conquered the whole island in 1822 and held it until 1844, when forces led by Juan Pablo Duarte, the hero of Dominican independence, drove them out and established the Dominican Republic as an independent state. In 1861, the Dominicans voluntarily returned to the Spanish Empire; in 1865, independence was restored. Economic difficulties, the threat of European intervention, and ongoing internal disorders led to a U.S. occupation in 1916 and the establishment of a military government in the Dominican Republic. The occupation ended in 1924, with a democratically elected Dominican Government...
Since 1996, the Dominican electoral process has been seen as generally free and fair. In June 1996, Leonel Fernández Reyna of the Dominican Liberation Party (PLD) was elected to a 4-year term as president. Fernández's political agenda was one of economic and judicial reform. He helped enhance Dominican participation in hemispheric affairs, such as the OAS and the follow up to the Miami Summit. On May 16, 2000, Hipólito Mejía, the PRD candidate, was elected president in another free and fair election, soundly defeating PLD candidate Danilo Medina and former president Balaguer. Mejía championed the cause of free trade and Central American and Caribbean economic integration. The Dominican Republic signed a free trade agreement (CAFTA-DR) with the United States and five Central American countries in August 2004, in the last weeks of the Mejía administration. During the Mejía administration, the government sponsored and obtained anti-trafficking and anti-money-laundering legislation, sent troops to Iraq for Operation Iraqi Freedom, and ratified the Article 98 agreement it had signed in 2002. Mejía faced mounting domestic problems as a deteriorating economy--caused in large part by the government’s measures to deal with massive bank fraud--and constant power shortages plagued the latter part of his administration.
During the Mejía administration, the Constitution was amended to permit an incumbent president to seek a second successive term, and Mejía ran for re-election. On May 16, 2004, Leonel Fernández was elected president, defeating Mejía 57.11% to 33.65%. Eduardo Estrella of the PRSC received 8.65% of the vote. Fernández took office on August 16, 2004, promising in his inaugural speech to promote fiscal austerity, to fight corruption and to support social concerns. Fernández said the Dominican Republic would support policies favoring international peace and security through multilateral mechanisms in conformity with the United Nations and the OAS. The Fernández administration has worked closely with the United States on law enforcement and immigration and counter-terrorism matters. On May 16, 2006, President Fernández’s PLD won a majority of seats in the upper and lower houses of Congress as well as a plurality of mayoral seats, marking a major shift in power among the main political parties. Several candidates have begun campaigning for the 2008 presidential elections, in which President Fernández is expected by many to run again.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon

