Republic of Slovenia
Related Categories:
 Slovenia Coat of Arms
Slovenia Coat of Arms |
Flag, Coat of Arms, Anthem.
www.dz-rs.si/
Use and History of the Flag, Coat of Arms.
www.fotw.us/
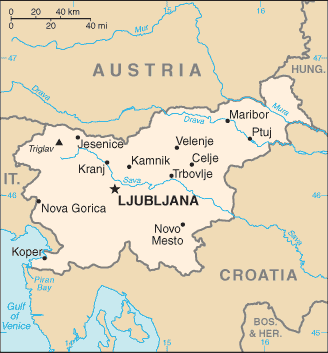
Four major European geographic regions meet in Slovenia: the Alps, the Dinarides, the Pannonian plain, and the Mediterranean.
en.wikipedia.org/
Slovenia is situated at the crossroads of central Europe, the Mediterranean, and the Balkans. The Alps--including the Julian Alps, the Kamnik-Savinja Alps, the Karavanke chain, and the Pohorje Massif--dominate northern Slovenia near Austria. Slovenia's Adriatic coastline extends for approximately 50 kilometers (39 mi.) from Italy to Croatia. The term "karst"--a limestone region of underground rivers, gorges, and caves--originated in Slovenia's Karst plateau between Ljubljana and the Italian border. On the Pannonian plain to the east and northeast, toward the Croatian and Hungarian borders, the landscape is essentially flat. However, the majority of Slovenian terrain is hilly or mountainous, with around 90% of the surface 200 meters or more above sea level.
The majority of Slovenia's population is Slovene (over 83%). Hungarians and Italians have the status of indigenous minorities under the Slovenian constitution, which guarantees them seats in the National Assembly. Most other minority groups, particularly those from the former Yugoslavia, immigrated after World War II for economic reasons. Slovenes are predominantly Roman Catholic, though the country also has a small number of Protestants, Orthodox Christians, Muslims, and Jews. Slovene is a Slavic language, written in the Roman script.
www.state.gov/r/
Introduction
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon
About
Contact
Symbols in The News
Interpret this Symbol
AAC
African
AI
Alchemy
Alphabets
Ancient
Animal Symbolism
Architecture
Art
Articles
Astrology
Baha'i
Blissymbolics
Blueprint Symbols
Buddhist
Celtic Symbols
Cemetery
Chinese Symbols
Christian
Circle
City
Codes
Color
Conlangs
Crop Circles
Danger
Da Vinci Code
Designing Logos
Dictionaries
Dreams
Education
Egyptian Symbols
Electrical
Emoticons
Find Images
Fonts
Food
Fraternity
Hamsa
Healing
Heraldry
Hermetic
Highway Signs
Hindu
History
Hobo
Holiday
Icons
iConji
Islamic
Jain Symbols
Japanese, Kanji
Jewish
Justice
Law
Literary Symbolism
Mandalas
Map
Masonic
Math, Number
Meaning of Names
Medical
Middle East
Military
Miscellaneous
Money
Music
Mythology
Native American
Playing Cards
Power
Psychology
QiQiiKhu
Reiki
Religious
Runes, Norse
Sacred Geometry
Scientific
Science Fiction
Sorority
Sports
Symbols in the News
Tattoos
ThirteenSymbols
Tree of Life
Ursprache
Videos
Visual Languages
Weather
Web Codes
Wicca
Words
Writing Systems
Braille
Coinherence
Coptic
Cuneiform
Easter Island
Etruscan
Happy Human
Hebrew
Kokopelli
Linear B
Lotus
Love Symbols
Mandorla
Moon Alphabet
Nine Pointed Star
Om
Oz
Phonetic
Scarab Beetle
Silent
Theosophy
Unifon

